 |
|||
|
|
|||
| ||||||||||
|
| 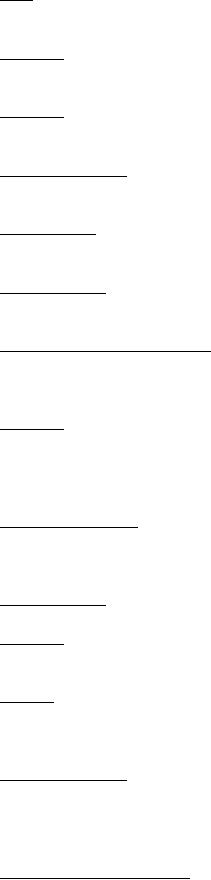 MIL-D-89009
Row. An ordered collection of fields pertaining to the
entity. A tuple in a relation.
Row id.
An integer that uniquely identifies each row in a
table.
Schema A description (or picture or diagram) of the
structures of a database system.
Schema table. A schema table defines the tables and their
relationships within a coverage.
Semantics. The implied meaning of data. Used to define what
entities mean with respect to their roles in a system.
Shape line. An ordered set of one or more coordinate tuples
that define the placement and shape of a text primitive.
Simple feature class. Consists of a single type of primitive
(face, edge, node, or text) and a feature table. There are four
subtypes of simple feature classes: point, line, area, and text.
Source. Source information describes the origin or
derivation of a single feature, primitive, or attribute. It
includes information about processing of the data as well as
information about the data source.
Spatial index. A data structure file that allows for the
rapid identification of a primitive by using the values of the
primitive's coordinates.
Start node.
The first node of an edge.
Syntax. The rules governing the construction of a machine
language or machine representation of entities.
Table. An organizational structure for data content. In the
relational model, a table is a group of repeating rows defined by
columns. Equivalent to a relation.
Text feature. A cartographic entity that relates a textual
description to a zero- or one-dimensional location. A text
feature usually contains information such as font, color, and
height.
Text feature class. A collection of text features that
maintains a homogenous set of attributes. Composed of text
primitives.
75
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |