 |
|||
|
Page Title:
Table 4C. Programming characteristics for circuit C. |
|
||
| ||||||||||
|
| 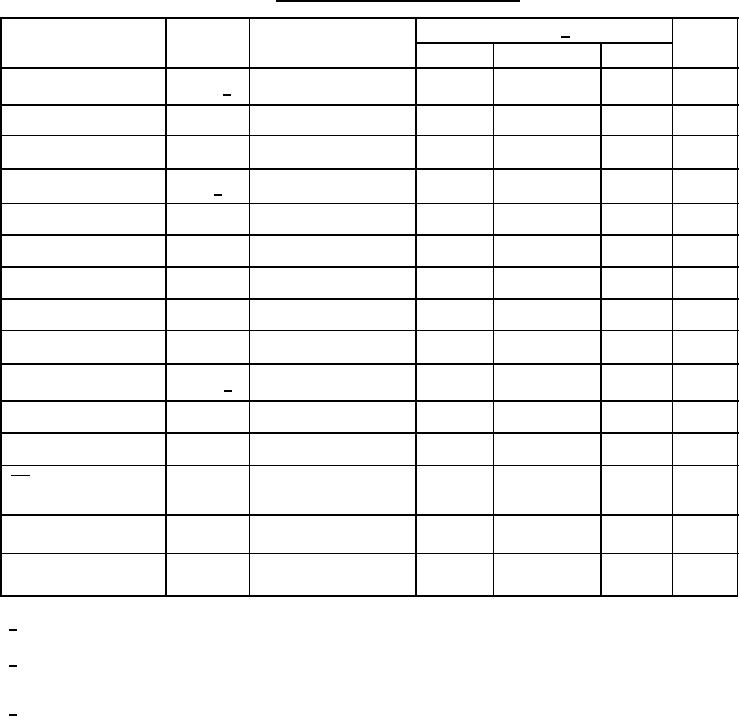 MIL-M-38510/207E
TABLE IVC. Programming characteristics for circuit C.
Limits 1/
Unit
Parameter
Symbol
Conditions
Min
Recommended
Max
Programming voltage to
ICCP = 375 75 mA;
9.5
10.0
10.5
V
VCCP 1/
VCC
transient or steady-state
Verification upper limit
5.3
5.5
5.7
V
VCCH
Verification lower limit
4.3
4.5
4.7
V
VCCL
Verify threshold
0.9
1.0
1.1
V
VS 2/
Programming supply
200
250
300
mA
VCCP = +8.75 0.25 V
ICCP
current
Input voltage high level
2.4
5.5
V
VIH
"1"
Input voltage low level
0
0.4
0.8
V
VIL
"0"
μA
Input current
50
IIH
VIH = +5.5 V
μA
Input current
-500
IIL
VIL = +0.4 V
Output programming
IOUT = 65 3 mA,
15.0
15.5
16.0
V
VOUT 3/
voltage
transient or steady-state
Output programming
62
65
68
mA
VOUT = +17 1 V
IOUT
current
Programming voltage
μs
10
50
tTLH
transition time
CE programming pulse
μs
300
400
500
tP
width
μs
Pulse sequence delay
10
tD
tPR /
Programming duty cycle
50
%
tPR + tPS
1/ Bypass VCC to GND with a 0.01 μF capacitor to reduce voltage spikes.
2/ VS is the sensing threshold of the PROM output voltage for a programmed bit. It normally constitutes the
reference voltage applied to a comparator circuit to verify a successful fusing attempt.
3/ Care should be taken to insure the 17 1 V output voltage is maintained during the entire fusing cycle.
The recommended supply is a constant current source clamped at the specified voltage limit.
29
|
|
Privacy Statement - Press Release - Copyright Information. - Contact Us |